- Home
- About Us
- Products
- Solutions
-

- Solutions by Industry
- Overview
-
- Solutions by Business Function
- Finance and Accounting
- Human Resource Management
- Purchase Management
- Operations Management
- Asset & Inventory Management
- Knowledge Management
- CRM - Customer Service, Call Center & Sales Automation
- Security & Surveillance
- BI and Data Warehousing
- Geo-Spatial Services & Solutions
- GIS based Turnkey Solutions
- Surveys
-
- Microsoft Dynamics Business Solution
- Overview
- Our Offerings
- Product Capabilities
- Industry Specific
-
- Services
- Clients
- Contact Us
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) Survey aids in Geo-referencing, Topographical Mapping and Image Processing which constitutes as integral components of modern geospatial data collection and analysis. It is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances to the Earth's surface.
- i. LiDAR sensors emit laser beams towards the ground and the time it takes for the laser pulses to return is used to calculate the distance to objects on the Earth's surface.
- ii. LiDAR surveys can create highly detailed 3D maps of terrain, vegetation, buildings and other features by collecting millions of these distance measurements.
- iii. LiDAR data is utilized in various applications which includes forestry, urban planning, flood risk assessment, infrastructure planning and natural resource management.
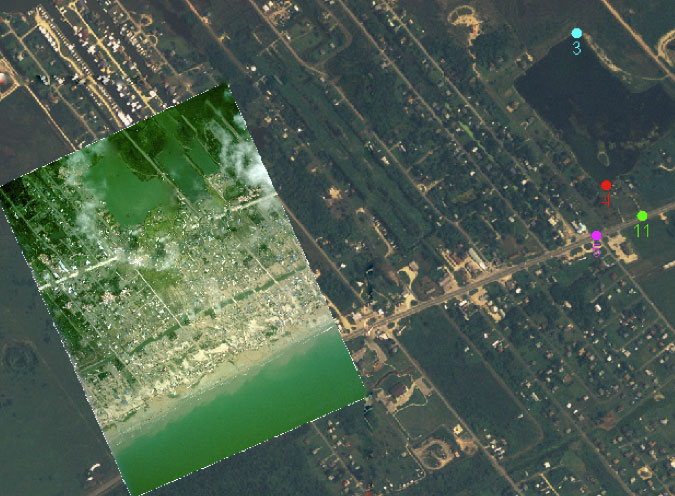
Geo-referencing:
- Geo-referencing involves aligning spatial data such as LiDAR point clouds or aerial imagery with real-world coordinates to ensure accuracy and compatibility with other datasets.
- This process typically involves referencing the spatial data to known geographic coordinates which uses ground control points, GPS measurements and satellite imagery.
- Geo-referencing enables spatial data to be accurately integrated into Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and used for mapping, analysis and decision-making.

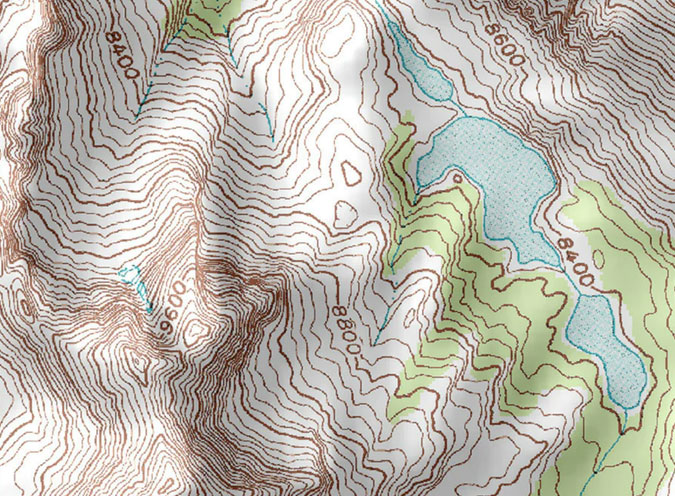
Topographical Mapping:
- Topographical mapping utilizes elevation data derived from LiDAR surveys to create detailed maps showing the shape and features of the Earth's surface.
- LiDAR-derived elevation models can accurately represent terrain features such as hills, valleys, ridges and drainage patterns.
- These maps are essential for various applications, including land use planning, engineering design, slope stability analysis and natural hazard assessment.
Image Processing:
- Image processing techniques are used to enhance and analyze aerial or satellite images for various purposes.
- This may involve applying filters, algorithms and statistical methods to improve image quality, remove noise and for extraction of relevant information.
- Image processing is used in applications such as land cover classification, change detection, object detection and environmental monitoring.
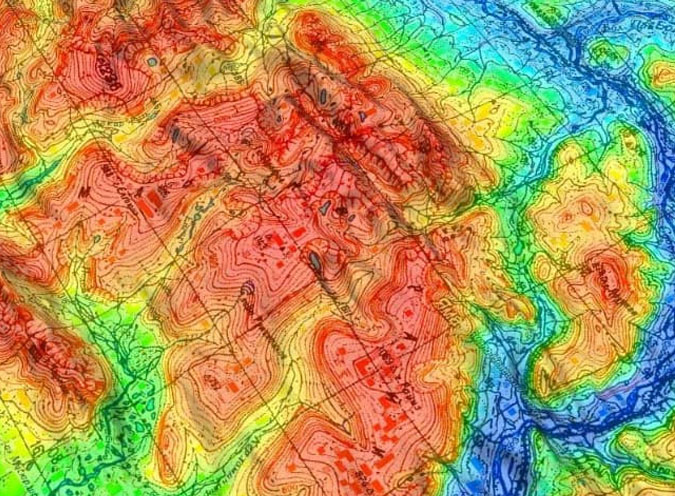
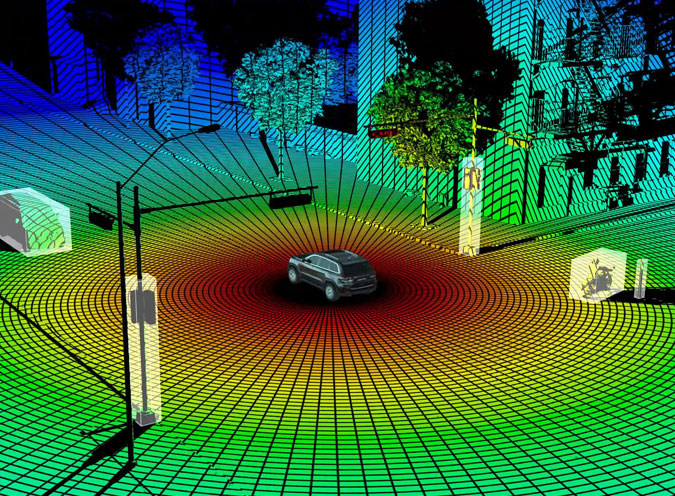
Importance and Applications:
- LiDAR surveying comprises of geo-referencing, topographical mapping and image processing which play a crucial role for a wide range of applications across industries.
- These processes provide valuable spatial data and insights that support decision-making in fields such as urban planning, natural resource management, environmental monitoring, infrastructure development and disaster management.
- By leveraging LiDAR technology and image processing techniques, organizations can accurately map and analyze the Earth's surface, identify spatial patterns and trends thereby facilitating informed decisions to address complex challenges and opportunities.


